
The recent evolutions of autonomous driving and its impact on vehicles’ interiors

Autonomous driving has evolved significantly these years along with the evolution of Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS). While not yet directly applied in fully autonomous passenger cars, autonomous driving systems are increasingly utilized in logistics, retail, industrial parks, and tourist attractions, where conditions can be more closely monitored and managed. Helen Cai, Innovation Marketing Director for FORVIA Interiors business group, shares with us insights and illustrations of what's happening now in the automotive industry.
What’s new on Autonomous Driving?
Car manufacturers have recently announced their plans to release autonomous driving vehicles. Tesla has officially posted that their Robotaxi "CyberCab" will be unveiled in October 2024. Rimac announced in June its first robotaxi service to be launched in 2026. Meanwhile, Renault's “Mach 2 project” will reveal a fleet of automated electric minibuses integrated into the public transport network of Châteauroux Métropole (France) from 2026 onwards. Nissan has also announced its plan to launch autonomous-drive mobility services in 2027 to serve multiple cities, including rural areas in Japan.
Who will drive your next car?
Autonomous driving technology evolves progressively through levels while reducing involvement of human beings.
- From Level 1 to Level 2, drivers benefit from systems that control both steering and acceleration/braking simultaneously, though they must remain alert.
- Moving from Level 2 to Level 3, the vehicle can handle all driving tasks under specific conditions, with the driver ready to intervene if needed.
- From Level 3 to Level 4, the car can manage all functions and address special conditions independently within defined areas, but manual control is still possible.
- At Level 5, full automation is achieved, eliminating the need for any human intervention, and making traditional driving controls unnecessary.
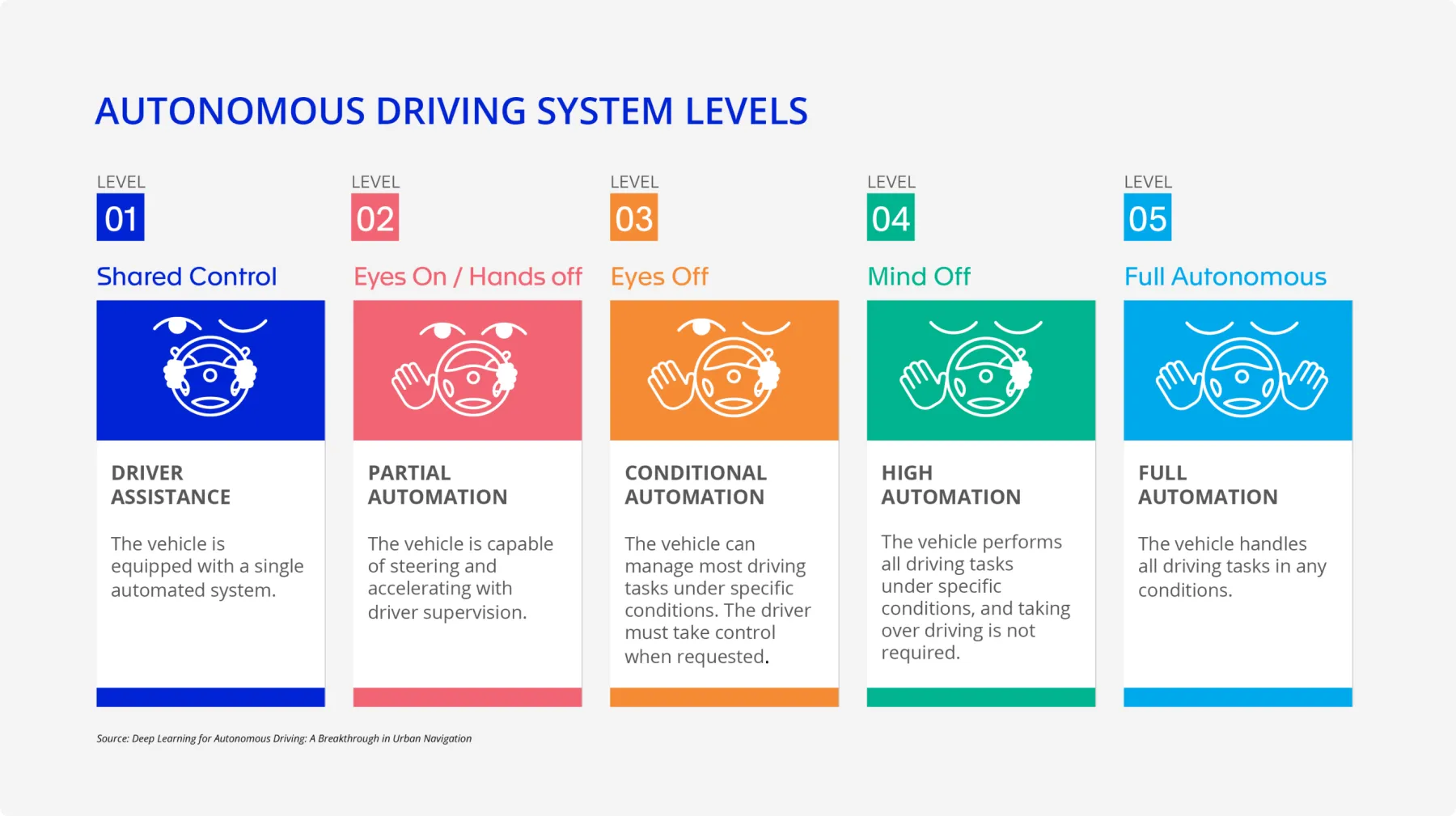
When the autonomous system is at Level 2 or below, full attention on the road is still required to drivers, even with all driving support systems engaged. Many car manufacturers have developed technologies to support Level 2 or Level 2+ autonomous driving needs. Examples include Tesla’s Autopilot with "Full Self-Driving," Audi’s "Traffic Jam Assist," and BMW’s "Extended Traffic Jam Assistant."
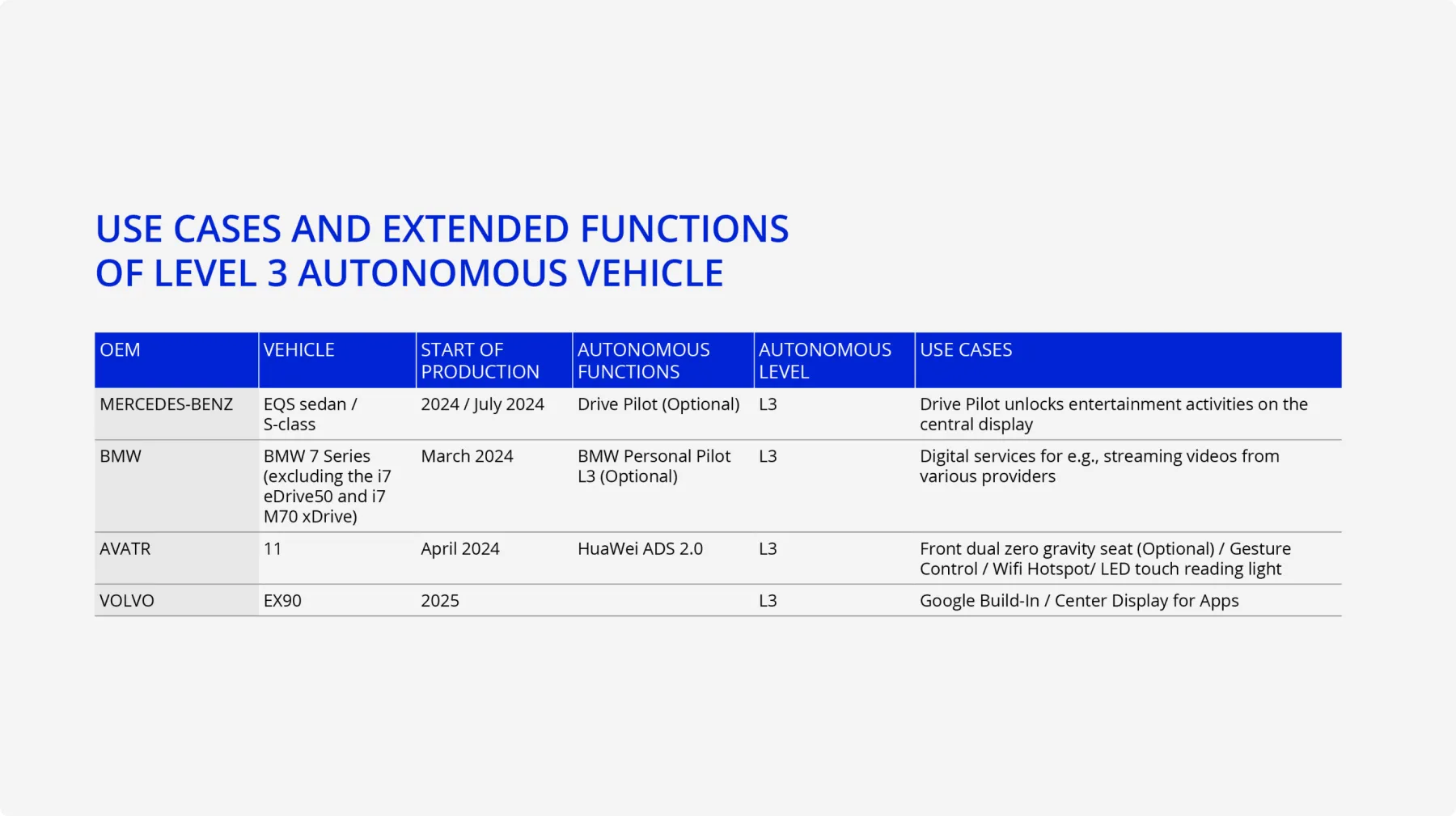
With the shift of vehicle control from human drivers to autonomous systems at Level 3 and above, responsibility and liability are also transferred to the machine. Car manufacturers are responsible for any potential accidents that occur while the vehicle's "Eyes Off" mode is in use. Additionally, the operation of Level 3 systems requires official certifications and approvals. In the United States, Mercedes-Benz's "Drive Pilot" is the first authorized Level 3 autonomous vehicle, permitted to operate on certain freeways at speeds up to 40 miles per hour. Level 4 and 5 autonomous vehicles can operate without human intervention but only in authorized conditions. Level 3 and above are subject to more strict liability frameworks, including safety standards and insurance requirements.
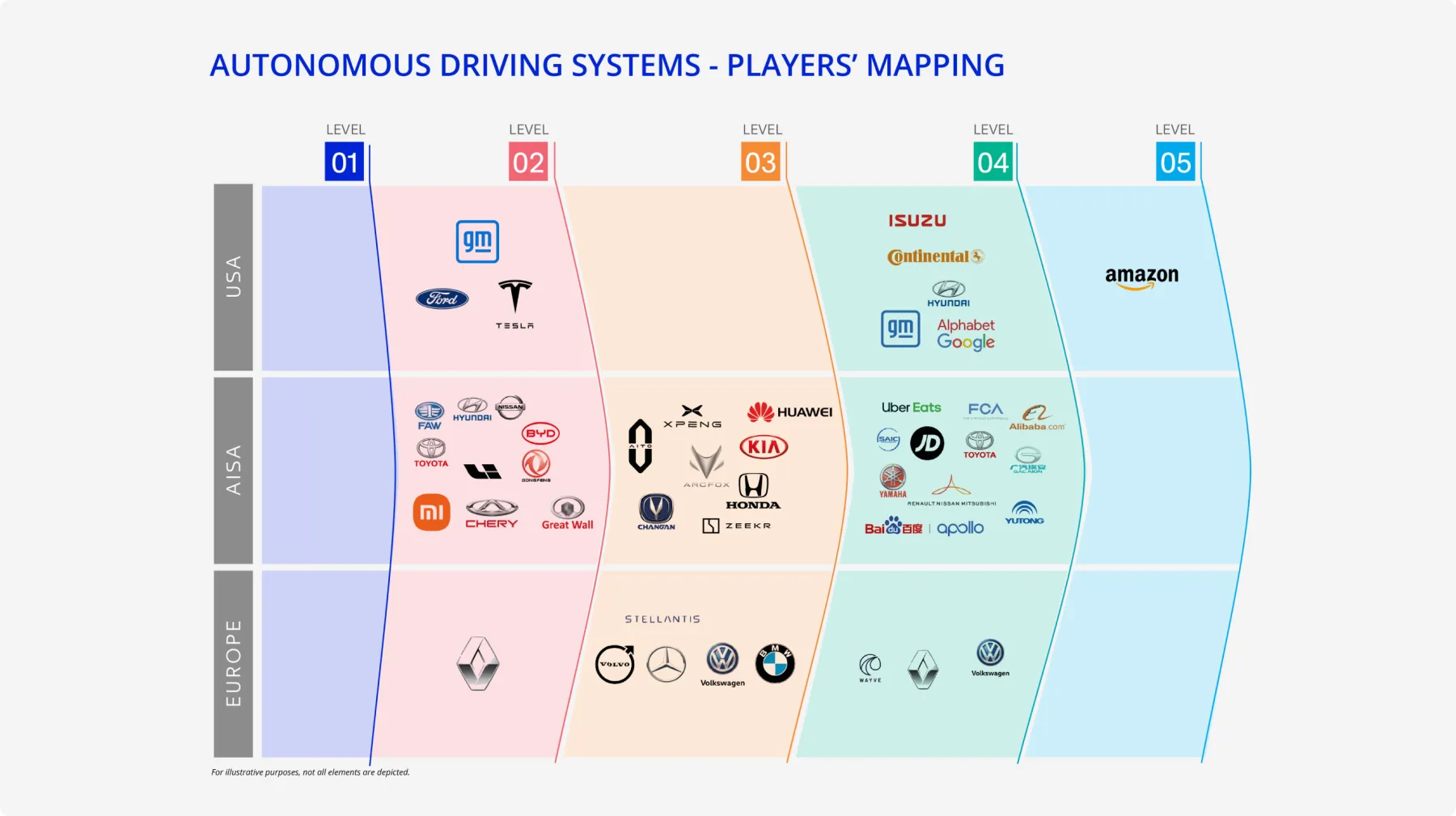
Who are the key players investing in autonomous driving ?
In 2024, 90% of European-made and American-made vehicles will offer Level 1 autonomous driving features, such as adaptive cruise control (ACC) and lane-keeping assist (LKA). Most car manufacturers are concentrating their efforts on the development of Level 2 and Level 3 autonomous driving vehicles. Some manufacturers, despite having Level 3 technologies, have not yet announced any authorized vehicles that can adopt the Level 3 system. Honda's Sensing Elite is an example. Honda's Sensing Elite offers Traffic Jam Pilot and Emergency Stop Assistant. Traffic Jam Pilot takes control of accelerating, braking, and steering while monitoring the vehicle’s surroundings on behalf of the driver when the vehicle gets caught in traffic congestion under certain conditions. Emergency Stop Assistant would change the lane and park the vehicle on the shoulder of the road, using hazard lights and the horn to alert other vehicles when the driver does not respond to the requests to transfer control back to the driver.
Additionally, car makers such as BMW, Hyundai-Kia, and Stellantis have outlined plans to incorporate Level 3 technologies into their vehicles around 2024. In the Level 4 & 5 Autonomous Market, traditional OEMs are not the only players. Besides OEMs like GM (Cruise) making moves in this market, there are also Big Tech companies such as Google (Waymo) and Amazon (Zoox), and ride-hailing services like Uber and Didi. These companies often form joint ventures and strategic partnerships to develop their own solutions.
What habits autonomous driving change from our mobility experiences?
With the implementation of Level 3 autonomous systems, drivers can take part in additional activities while in the vehicle. The Mercedes-Benz Drive Pilot L3 system lets drivers remove their hands from the steering wheel and take their eyes off the road under specific conditions. This technology permits engagement in activities such as gaming, video watching, or dining in transit. Similarly, the BMW Personal Pilot L3 system allows drivers to concentrate on secondary tasks while moving within Geo-Fenced[1] areas, including email correspondence or phone calls. Furthermore, digital services such as video streaming can be utilized on the central screen during routine highway commutes.
The evolution of autonomous vehicles requires significant changes in vehicle interiors. FORVIA, the world’s 7th largest automotive technology supplier, through its Cockpit of the Future team, is developing innovations focusing on providing a safer, more comfortable and personalized journey while travelling in an autonomous driving vehicle.
From smart surfaces, innovative HMI, safety and wellness applications to full cabin infotainment with pillar-to-pillar displays, FORVIA works on a full range of technologies integrated in vehicle interiors to adapt to different levels of autonomous driving conditions, including radars and by-wire applications with Hella. Modular and upgradable cockpit architecture enables upgrade of features depending on driving and non-driving use cases, such as upgradable central display and retractable steering wheel. Smart and multi-function sliding center console is another key cabin element which converts the vehicle cabin into living room in autonomous driving mode. Surface activation solutions as lighting, heating, viewing, and sensing improves non driving experience to be more intuitive and user friendly. While the User Experience was on driving an engine, it is now shifting to the numerous possibilities and comfort that a car interior can offer. Car interiors are transforming themselves into the extension of one’s living room.
And it is only the beginning of a long journey.
What about the ultimate Level 4+?
Furthermore, RoboTaxi and Level 4 autonomous vehicle can allow consumers to achieve “Mind Off” inside vehicles. As presented in Beijing Auto Show in April 2024, the Level 4 VW ID CODE concept provides occupants with a range of options, including the ability to read, go online, watch movies, or arrange the seats in a way that allows for sleep. Under Level 4 mode, the VW ID CODE offers a retractable steering wheel, which creates additional space. The rotatable front seats provide an optimal seating arrangement for the occupants in the front, allowing them to face each other and engage in conversation.
Car manufacturers explore Level 4 autonomous vehicles into the RoboTaxi or RoboBus sector by launching their own services or investing in existing ride-hailing platforms. For example, GM has invested in Lyft for about $500 million in 2016 for driverless vehicles, while Toyota has invested $500 million in Uber and $1 billion to Grab in 2018, and Tesla is developing its own ADAS system. RoboTaxis are allowed to operate within limited Geo-Fenced Areas according to local regulations. Compared to normal vehicles, RoboTaxi business model allows possibilities to offset the cost of expensive sensors required by operating autonomous taxi services.
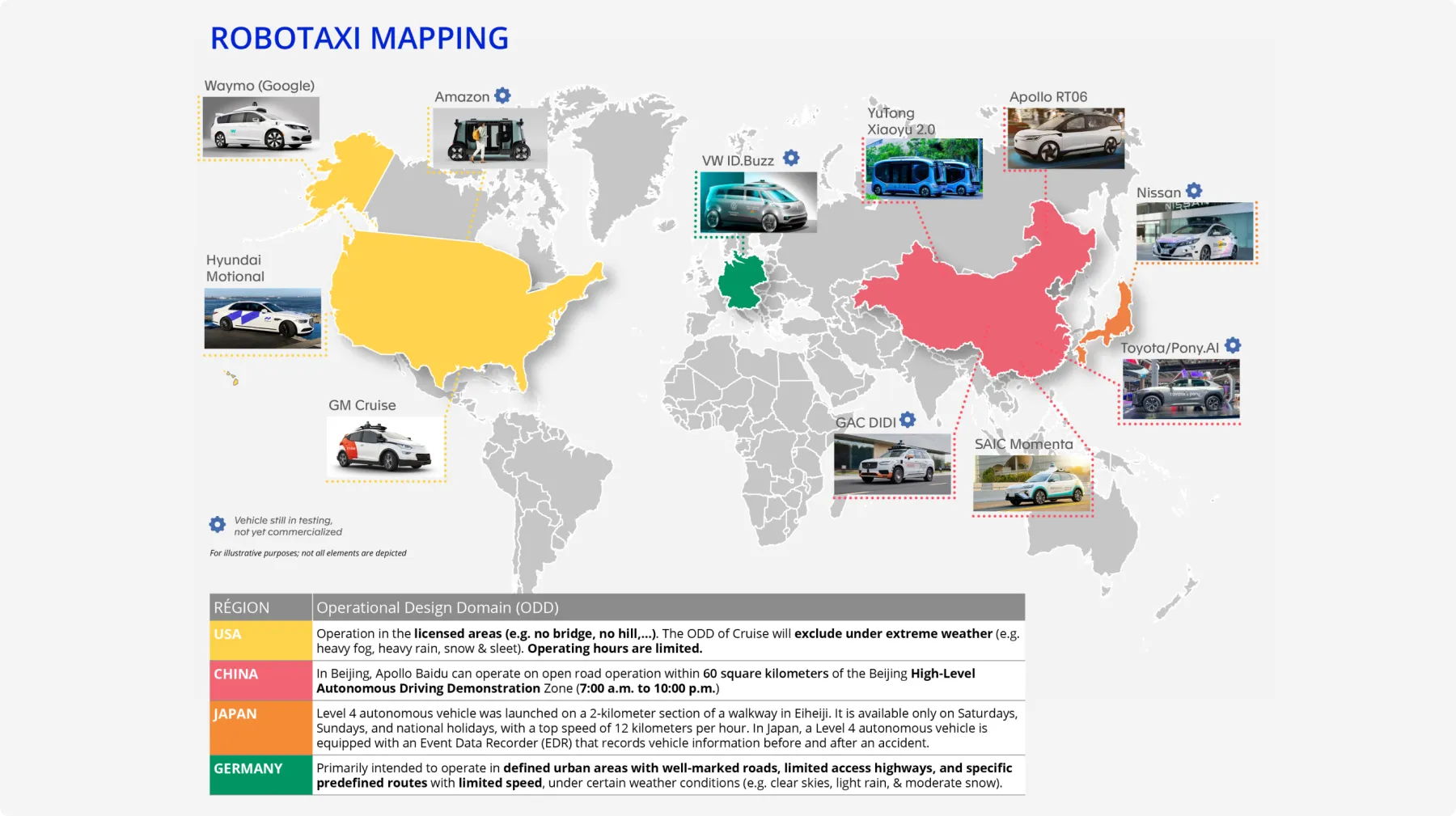
Global collaborations and partnerships
Car manufacturers are starting to form alliances to advance autonomous vehicle technologies and access advanced technologies without incurring high costs and risks. GM has partnered with Cruise and invested about $8 billion in Cruise since 2016. Hyundai works with Aurora to develop Level 4 autonomous vehicles. Some manufacturers, like Fiat Chrysler and Volvo, license technology from companies like Waymo instead of creating it in-house.
In the meantime, the development of autonomous vehicle technology varies across regions. In Asia, countries like Japan and China invest heavily in autonomous vehicle technologies. China aims for 50% of new auto sales to include automation by 2025 and invests in infrastructure like 5G networks to support autonomous vehicles. States such as California and Arizona have become testing hubs in the United States due to flexible regulatory environments. Major tech companies like Google and Amazon also invest in these technologies and form alliances to drive innovation.
Advancement of regulations
Regulations are crucial in the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles. In Germany, the 2021 Autonomous Driving Act enables Level 4 vehicles to be tested in real traffic scenarios. Germany aims to integrate Level 4 and 4+ vehicles into its transport system by 2030, including autonomous trucks and connected driving technologies. In the United States, updated state laws regulate the commercial operations of Level 4 autonomous vehicles. States like Texas and California have regulations permitting Level 4 RoboTaxis from Cruise to operate in cities such as San Francisco and Austin.



