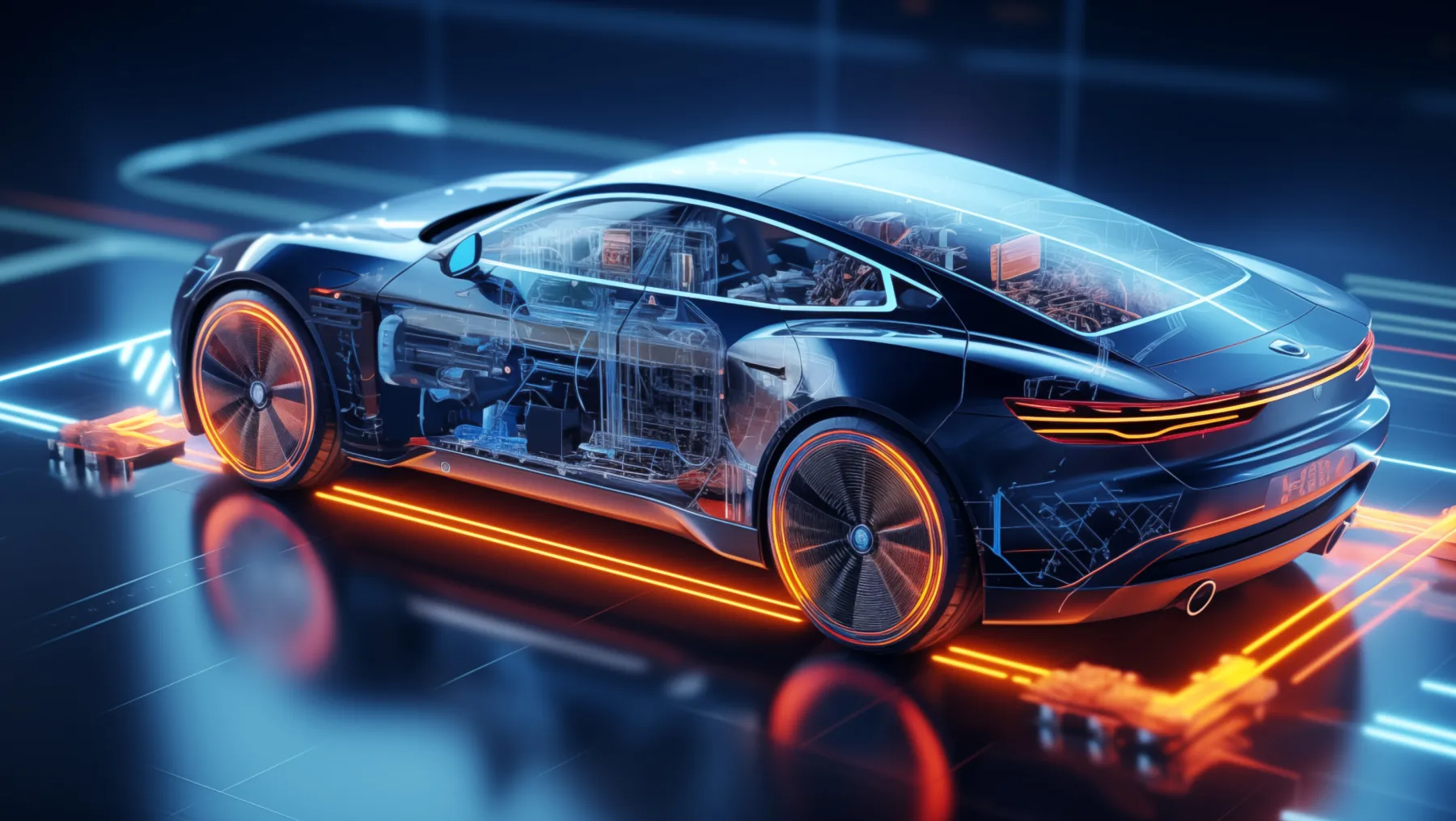
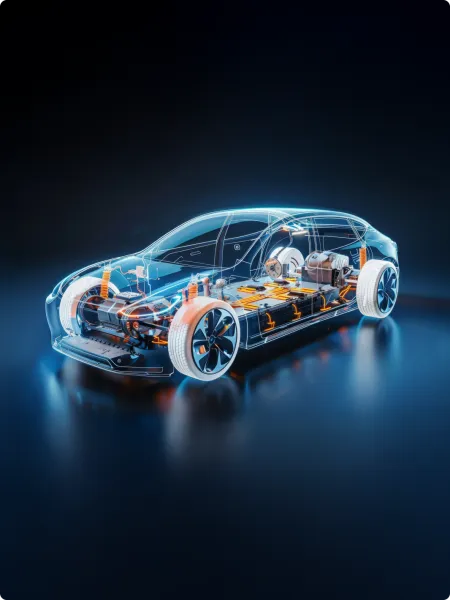
The key to powering electrified vehicles
Electric vehicles depend on a steady and stable source of electricity to move – but also to run the many systems that enable infotainment, driver assistance, and more. By optimizing battery charging and controlling both the power received and delivered, power management systems provide cars with the energy they rely on.
Deliver high power
Manage battery charge
Optimize battery lifetime
Recover energy
A power management solution adaptable to all powertrain architectures
Our industry leading expertise
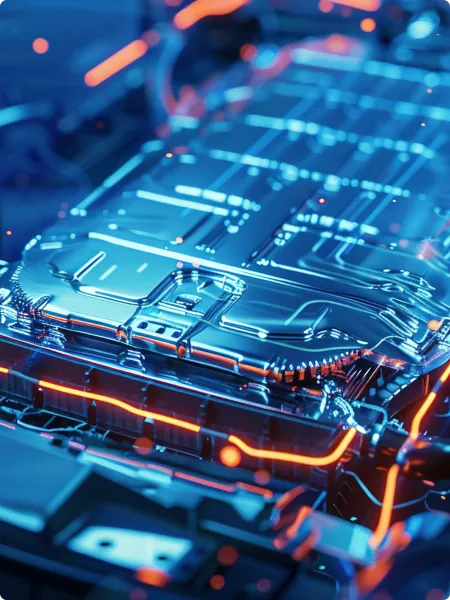
Proven leadership in power electronics
Providing cutting-edge power electronics solutions tailored for various power classes, FORVIA HELLA is a renowned market leader. Thanks to HELLA’s large purchasing volume of electronic and mechanical components, we are also able to achieve competitive prices.
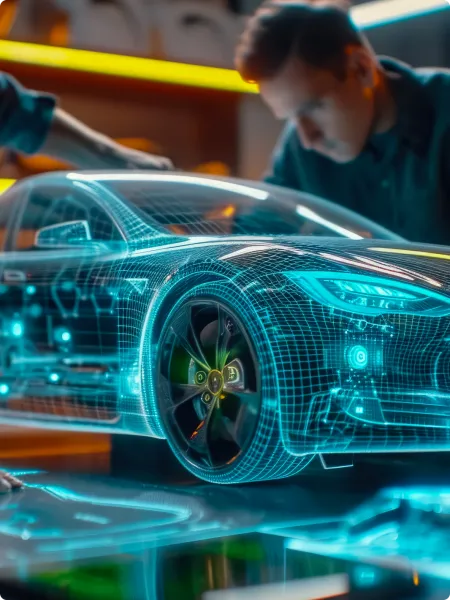
Certified excellence and commitment to quality
The quality of our solutions is validated through rigorous assessment processes, guaranteeing high reliability and compliance with the most demanding industry standards for power-related software development and functional safety. During development, we rely on our know-how and dedicated in-house high-voltage testing and analysis departments, as well as the support of our technology and process experts.
Our featured technologies
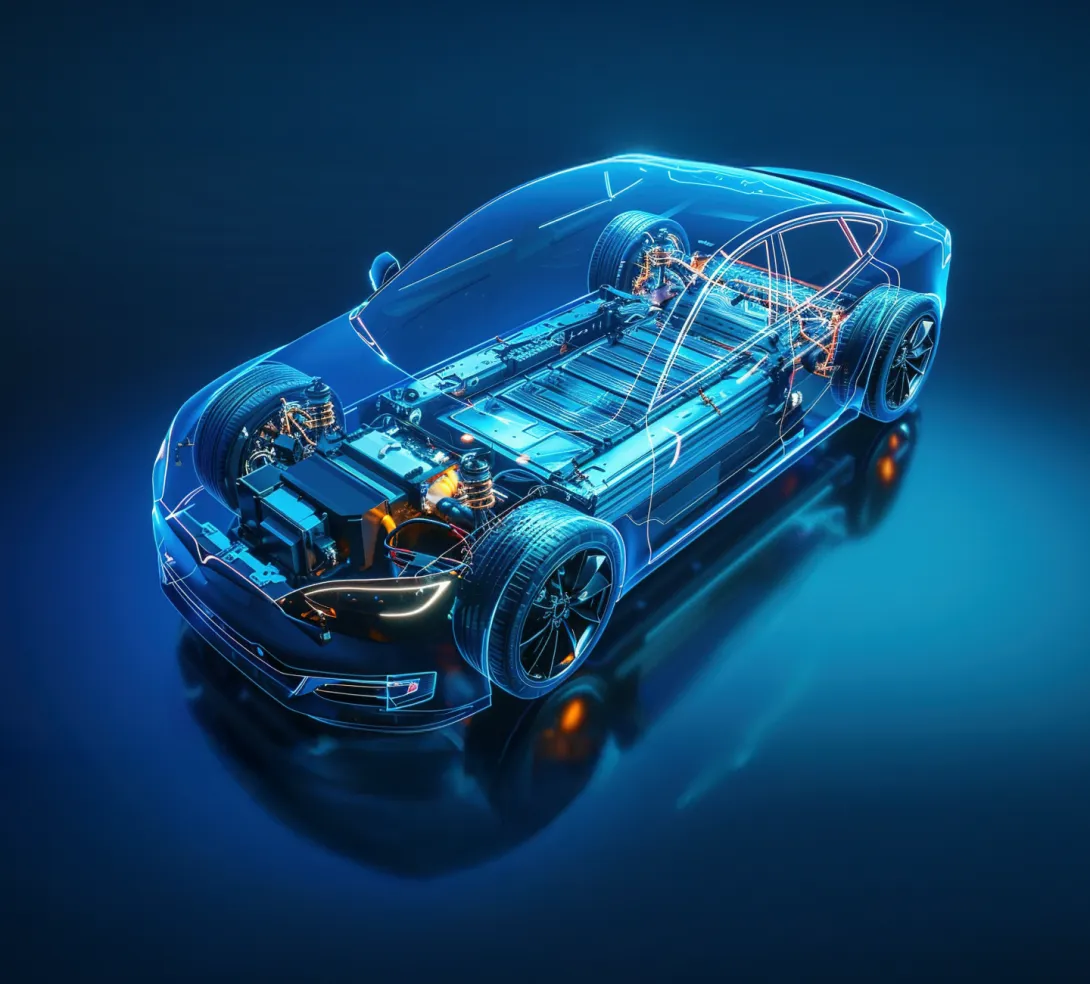

Battery Management System
Battery Management System
The Battery Management System is designed to monitor, control, and optimize the performance of a battery pack in an electrified or hybrid vehicle. To achieve this, it continuously tracks key battery parameters (voltage, temperature), balances the cells to extend their lifespan, and protects them against the risk of overheating.

DC/DC Converter
DC/DC Converter
The DC/DC Converter contributes to the energy management of an electrified vehicle by ensuring a stable and reliable power supply to the various electrical systems of the power management system. It adjusts the battery voltage for components operating at lower levels, supplies energy (lighting, sensors) to auxiliary systems, and minimizes electrical losses.


